About Me
I’m an undergraduate student at Johns Hopkins University pursuing a triple major in Computer Science, Electrical Engineering, and Computer Engineering, with minors in Robotics and Visual Arts. I’m a researcher in the JHU Social Cognitive AI (SCAI) Lab, advised by Prof. Tianmin Shu and Prof. Alan Yuille . I’m also fortunate to work at MIT’s Computational Cognitive Science Group(CoCoSci) and Probabilistic Computing Project(ProbComp), advised by Prof. Josh Tenenbaum and Prof. Vikash Mansinghka.
My research interest is to uncover the computational principles that fuse human-like visual perception with high-level cognitive reasoning and instantiate them in embodied AI systems that truly understand and interact with the real world. I’d like to design multi-modal models that blend vision with language-grounded probabilistic reasoning so agents can infer goals, causality, and affordances from sparse observations. By embedding these models in robots and photorealistic simulators, I aim to create agents that can plan, communicate, and collaborate with humans in open-ended environments.
Selected Publications
Yan Zhuang, Jiawei Ren, Xiaokang Ye*, Jianzhi Shen, Ruixuan Zhang, Tianai Yue, Muhammad Faayez, Xuhong He, Xiyan Zhang, Ziqiao Ma, Lianhui Qin, Zhiting Hu, Tianmin Shu
Abstract
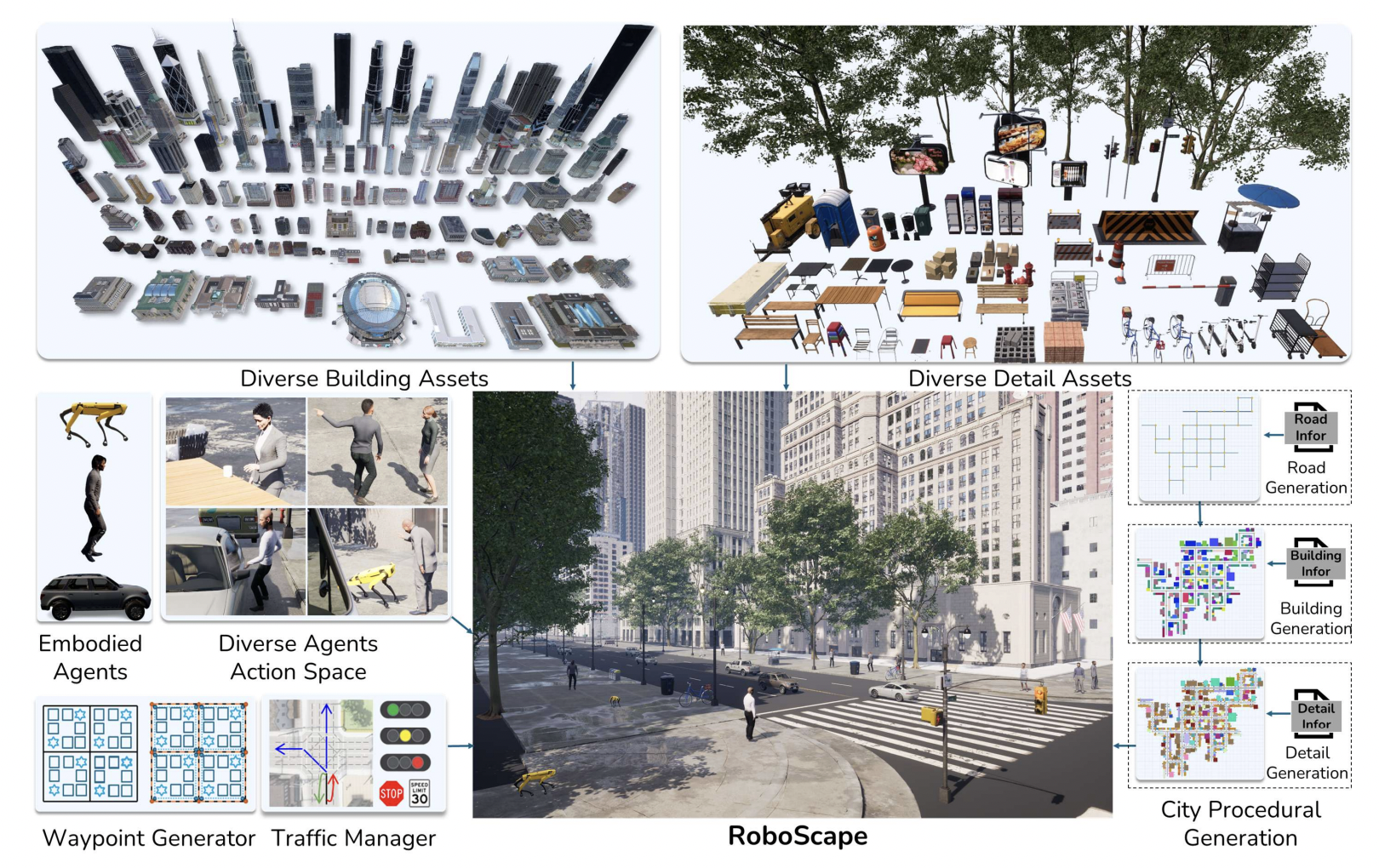
Recent advances in foundation models have shown promising results in developing generalist robotics that can perform diverse tasks in open-ended scenarios given multimodal inputs. However, current work has been mainly focused on indoor, household scenarios. In this work, we present RoboScape, a simulation platform for embodied AI in large-scale, photorealistic urban environments. Built on Unreal Engine 5, RoboScape procedurally generates unlimited photorealistic urban scenes populated with dynamic elements such as pedestrians and traffic systems, surpassing prior urban simulations in realism, complexity, and scalability. It also supports multi-robot control and communication. With these key features, we build two challenging robot benchmarks: (1) a multimodal instruction-following task, where a robot must follow vision-language navigation instructions to reach a destination in the presence of pedestrians and traffic; and (2) a multi-agent search task, where two robots must communicate to cooperatively locate and meet each other. Unlike existing benchmarks, these two new benchmarks comprehensively evaluate a wide range of critical robot capacities in realistic scenarios, including (1) multimodal instructions grounding, (2) 3D spatial reasoning in large environments, (3) safe, long-range navigation with people and traffic, (4) multi-robot collaboration, and (5) grounded communication. Our experimental results demonstrate that state-of-the-art models, including vision-language models (VLMs), struggle with our tasks, lacking robust perception, reasoning, and planning abilities necessary for urban environments.
GoLoColor: Towards Global-Local Semantic Aware Image Colorization
Tianai Yue, Xiangcheng Du, Jing Liu, Zhongli Fang
Abstract
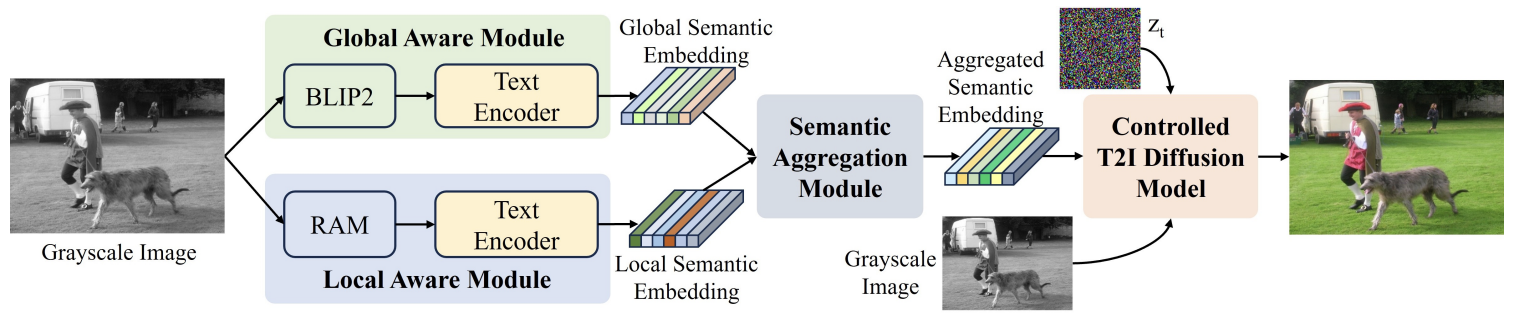
Owing to powerful generative priors, Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models have achieved promising results in image colorization task. However, recent advanced methods primarily integrate global semantics. Such practice neglects local semantics, yielding suboptimal colorization performance. In this paper, we present a novel global-local semantic aware colorization method named GoLoColor, which performs semantic awareness at both global and local levels. The GoLoColor includes Global Aware (GoA) module, Local Aware module (LoA) and Semantic Aggregation (SA) module for semantic understanding. Specifically, the GoA produces global semantic embedding to represent whole image, while the LoA provides semantic support for local objects, particularly in scenes containing multiple entities. The SA module facilitates semantic interaction between local and global semantic embedding to produce richer semantic information. Finally, a controlled T2I diffusion model is utilized to produce color image guided by the aggregated semantic embedding. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance and can produce realistic colorization.
Tianai Yue, Rongtao Xu, Jingqian Wu, Wenjie Yang, Shide Du, Changwei Wang
Abstract
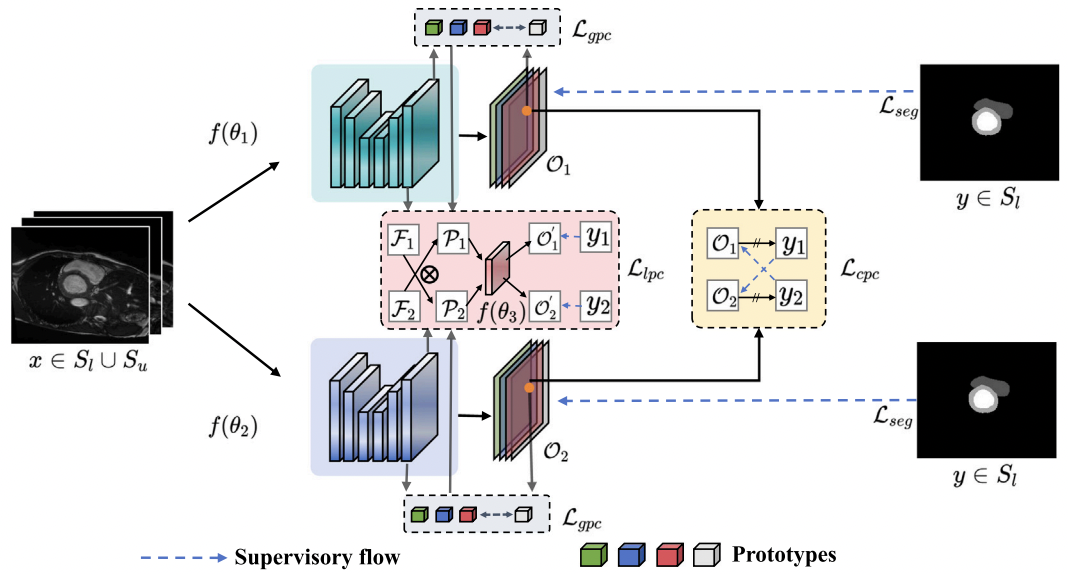
In medical intelligence applications, the labeling of medical data is crucial and expensive, so it becomes urgent to explore labeling-efficient ways to train applications. Semi-supervised techniques for medical image segmentation have demonstrated potential, effectively training models using scarce labeled data alongside a wealth of unlabeled data. Therefore, semi-supervised medical image segmentation is a key issue in engineering applications of medical intelligence. Consistency constraints based on prototype alignment provide an intuitively sensible way to discover valuable insights from unlabeled data that can motivate segmentation performance. In this work, we propose a Dual prototypes Contrastive Network to motivate semi-supervised medical segmentation accuracy by imposing image-level global prototype and pixel-level local prototype constraints. First, we introduce a Background-Separation Global Prototype Contrastive Learning technique that utilizes the natural mutual exclusivity of foreground and background to separate the inter-class distances and encourage the segmentation network to obtain segmentation results that are more complete and do not contain background regions. Second, we design a Cross-Consistent Local Prototype Contrastive Learning techniques to extend the perturbation consistency of the two networks to the prototype's localized response to the feature map, thereby shaping a more stable intra-class prototype space and producing accurate and robust pixel-level predictions. Finally, we comprehensively evaluate our method on mainstream semi-supervised medical image segmentation benchmarks and settings, and experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, our method achieves a Dice Coefficient score of 91.8 on the Automatic Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge dataset using only 10% labeled data training, 1.1% ahead of the second best method.
Enhancing Graph Neural Networks with Mixup-Based Knowledge Distillation
Tianai Yue, Jing Liu
Abstract
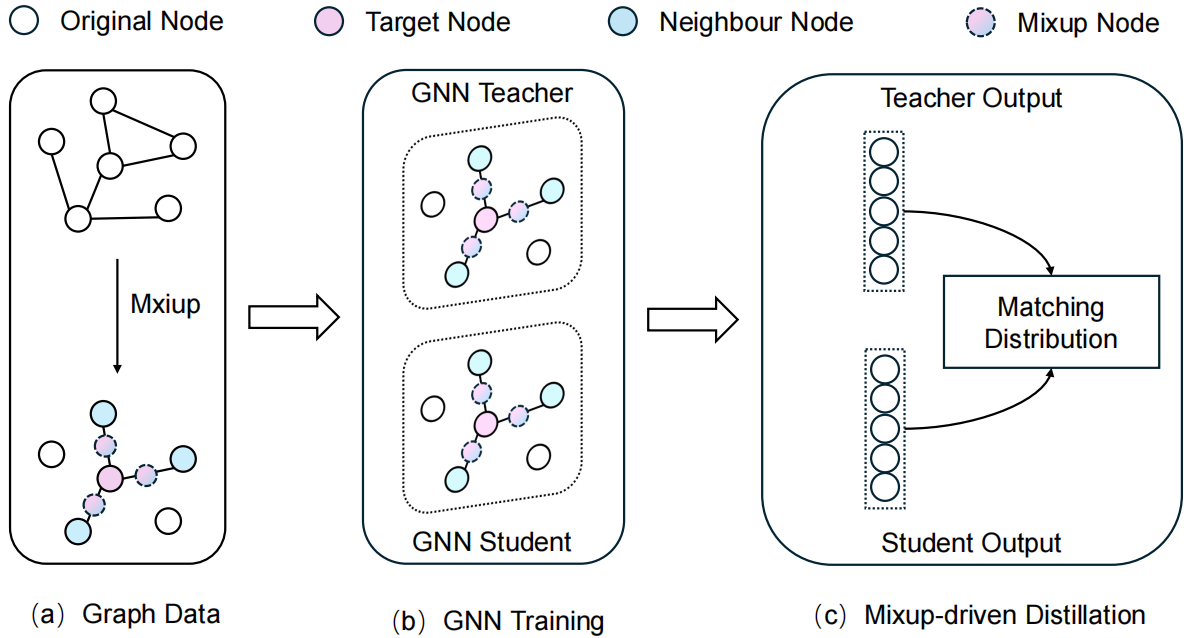
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in processing graphstructured data and have been widely adopted for various graph-related tasks. In recent years, graph knowledge distillation has emerged as an effective model optimization technique, achieving outstanding performance in enhancing GNN capabilities. However, it remains constrained by the inherent sparsity and dependency of graph data. To address this, we propose Mixup-driven Distillation for Graph Neural Networks (MD-GNN), an innovative framework that combines Mixup-based data augmentation with knowledge distillation to boost GNN performance. Specifically, we first leverages Mixup to perform linear interpolation on both node features and labels, generating diversified training samples while preserving original graph topology. Subsequently, based on these generated data, we extract knowledge from a pre-trained GNN teacher through output logit alignment to guide the training of student GNN models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MD-GNN significantly outperforms existing baseline GNN models, achieving performance gains of 2.54%-3.73% on three benchmark datasets (Cora, CiteSeer, and PubMed). Notably, MD-GNN exhibits superior generalization capabilities and enhanced robustness, particularly showing notable advantages in noisy scenarios.